Module 1
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet.
Advantages and disadvantages of Cloud Computing
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|
| Scalability and Flexibility | Security Concerns(storing sensitive data) |
| Cost Efficiency | Downtime and Reliability |
| Enhanced Security | Internet dependency |
| Improved collaboration and Accessibility | Cost management(pay-as-you-go model might overcharge if not used properly) |
| Easier maintenance and updates |
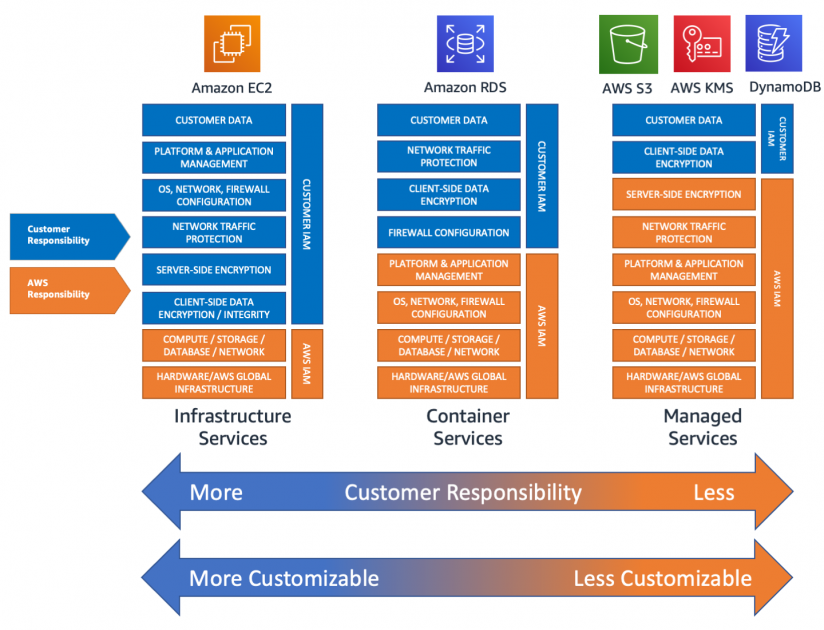
Cloud Service Models
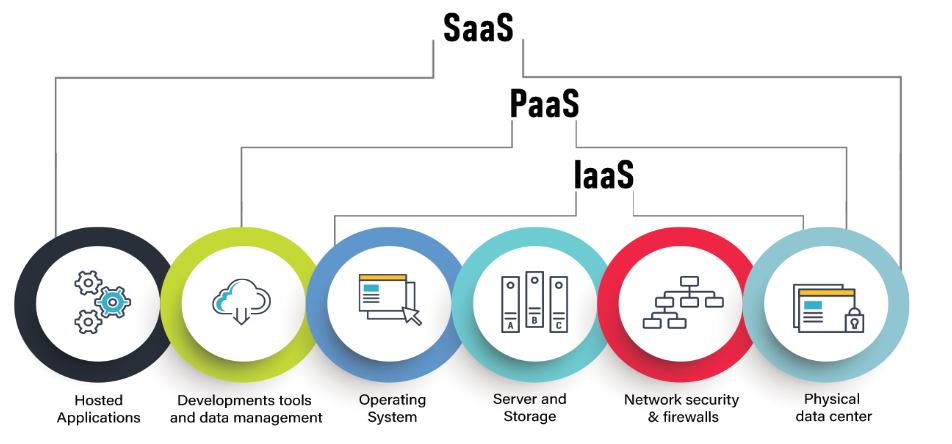
IaaS
Cloud Service Provider(CSP) provides infrastructure and resources. Customer manages everything else.
PaaS
CSP provides infrastructure and a development platform. This platform manages the underlying infrastructure and enables the customer to develop their own software.
SaaS
CSP has full control over infrastructure and software on the cloud. Customer simply rents these software.
Cloud Deployment Models
Public cloud
Services are delivered over the internet and are owned by third party providers Advantages: Minimal investment, No setup cost, Infrastructure management not required, no maintenance and dynamic stability. Disadvantages : Less secure and low customization.
Private cloud
Dedicated environment for a single user with no shared hardware. Can be hosted or on premises. Advantages: Better control, data security and privacy, supports legacy systems and customization. Disadvantages: Less scalable and expensive.
Hybrid cloud
Combines public and private cloud. 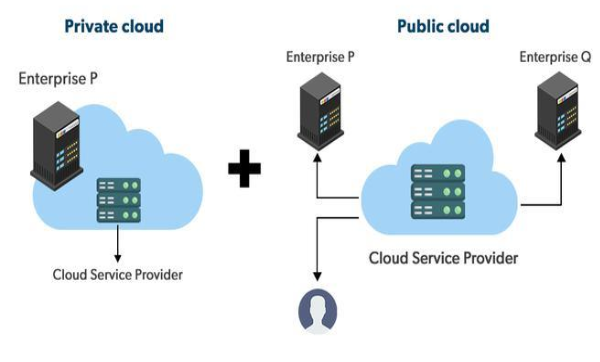 Advantages: Flexibility, scalability and cost efficiency. Has better disaster recovery options.
Disadvantages: Complex to manage and requires expertise in integrating and maintaining both public and private cloud. Security concerns raise over data transfer between private and public environment.
Advantages: Flexibility, scalability and cost efficiency. Has better disaster recovery options.
Disadvantages: Complex to manage and requires expertise in integrating and maintaining both public and private cloud. Security concerns raise over data transfer between private and public environment.
AWS Global Infrastructure
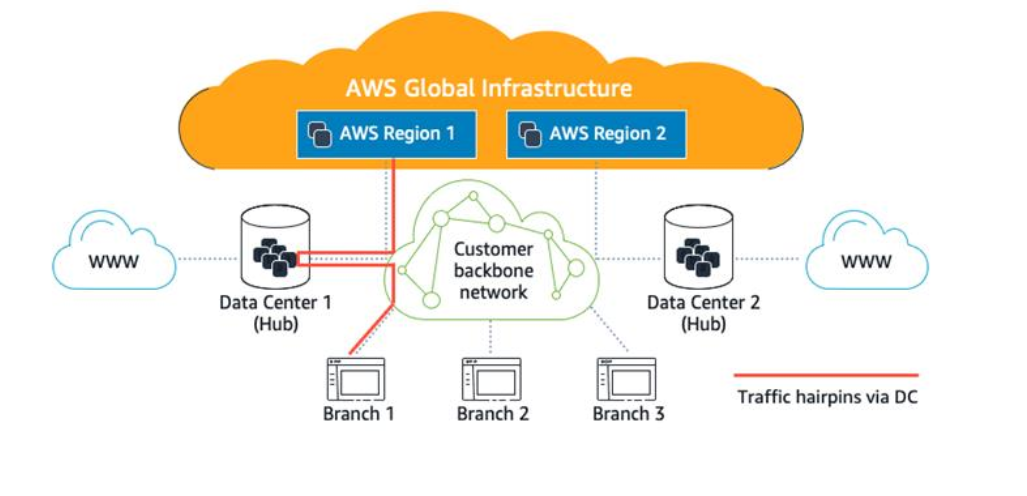
Availability Zones(AZ)
AZs are distinct data centers within a region, each with independent power, cooling, and networking to ensure fault isolation.
Regions
Regions are separate geographic areas with multiple AZs.
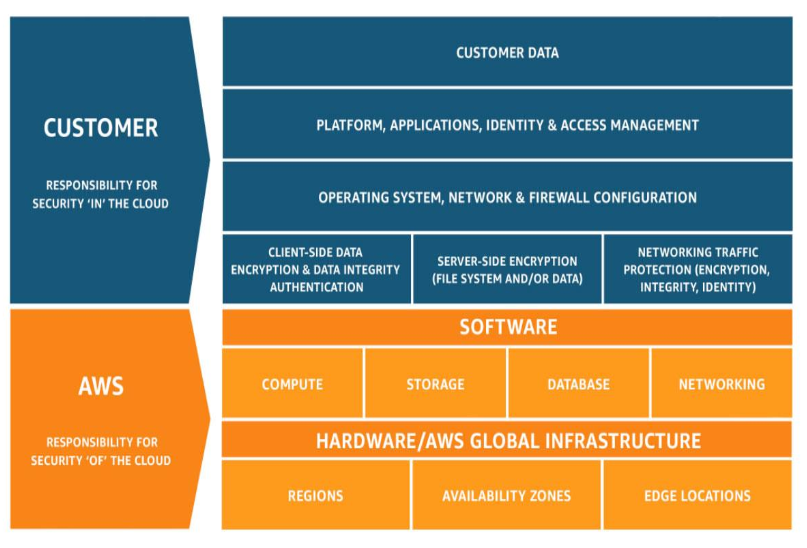
AWS Shared Responsibility Model