Module 2
Amazon EC2
Basically virtual machines. Scalable cloud compute service that allows users to run virtual servers known as instances in AWS data centers.
Features
- Elasticity and scalability
- Variety of instance types: Many instance types are there and can use AMI(Amazon Machine Image) as a template to create and launch new instances.
- Configurability
- Pay-As-You-Go pricing
- Easy integration with other AWS services
- Security
- Security groups act as firewalls for instances to control inbound and outbound traffic.
- Monitoring and management
- EBS(Elastic Block Storage) provides persistent block storage volumes for use with EC2 instances.
- Placement groups allow you to influence placement within AWS infrastructure(used to ensure low latency).
Benefits
- AWS Regions and AZs improve stability and reduce latency
- Use EC2 fleet to optimize scale, performance and cost.
- Elastic Fabric Adapter to run applications that require high levels of interinstance communications(basically an IPC)
- AWS Private Link to access other Amazon services.
- Regular maintenance done by AWS.
Pricing options
- Standard reserved instances(75% discount if long term)
- Convertible reserved instances(54% discount)
- Scheduled reserved instances
- Spot instances(cheapest)
Amazon S3
S3 means Simple Storage Service. Secure, scalable and high performance object storage service by AWS. High scalability. 11 nines stability(99.999999999%)
Key concepts
- Buckets are containers used for storing files. Each bucket is globally unique and can contain unlimited number of objects.
- Objects are individua files stored in S3. Each Object consists of the data, a unique key and optional metadata.
- Permissions and Access Control: S3 uses IAM and ACLs to manage data securely.
- Versioning: S3 allows versioning and keep multiple versions of the same object to protect against accidental deleting.
Advantages
- Scalable
- Durable
- Secure
- High availability
- Low cost
- Ease of integration with other AWS services
- Flexible storage options
Challenges
- Complex pricing
- Latency when accessing large datasets
- Complex access control with large teams
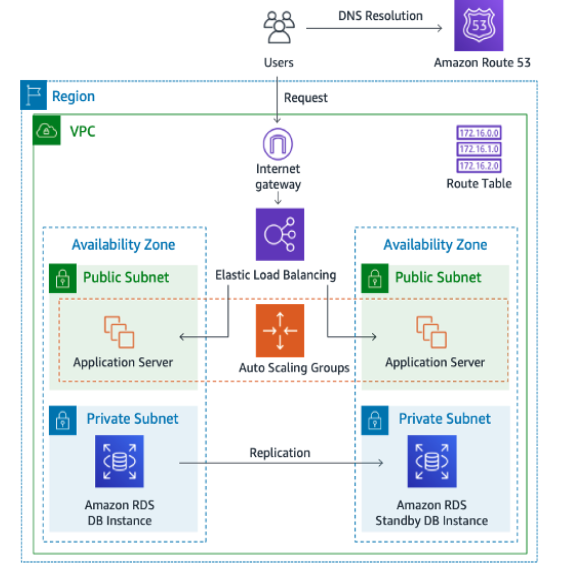
Amazon RDS
Relational Database Service is a fully managed database services that simplifies the setup, operation and scaling of relational databases in the cloud. MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MariaDB.
Components of RDS
- DB Instance: A VPS where the db runs.
- DB Engine: The RDBMS engine(like postgres or mysql)
- DB Storage: Storage used to store the data(usually EBS)
- DB Parameter Group: A collection of settings that control the behavior of the DB engine.
- DB Security Group: Firewall and access rules.
- Multi-AZ Deployment: Provides high availability by replicating data to a standby instance in another availability zone.
- Read Replicas: Used to offload read queries, improving performance for read-heavy
workloads.
Advantages
- High availability due to Multi AZ deployments.
- Scalability
- Security(encrypted data at rest and in transit)
- Monitoring and management using cloud watch
- Automated Backups
- Cost Effective(since it is managed service)
Challenges
- Vendor lock in
- limited control
- Performance for big data
Amazon VPC
Virtual Private Cloud allows users to create isolated, secure virtual networks within AWS
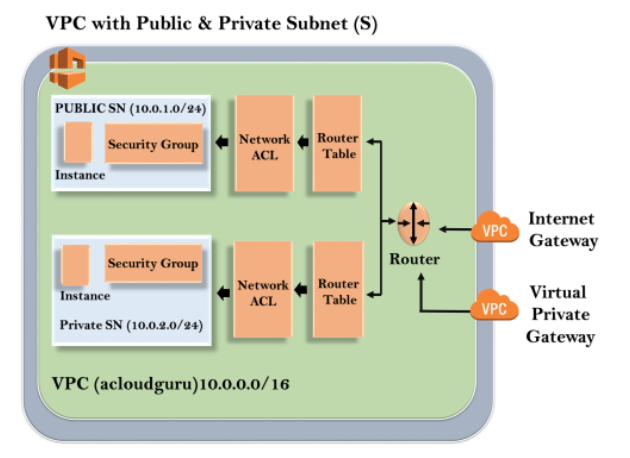
Key features
- Isolation
- Subnets: Can divide the VPC into public and private subnets for different groups
- Security
- Custom IP addressing(own private IP ranges and subnets)
- VPN connectivity
- Peering between VPCs
- Elastic IPs and NAT
Advantages
- Isolation and security
- Customizable network architecture
- Scalability
- Hybrid Cloud connectivity
- High availability
- Internet and private connectivity
- Cost control
Challenges of VPC
- Complex in config
- Network management overhead as VPCs grow in complexity
- Limited public IPs
- Latency and bandwidth constraints
- Peering limitations
- Cost of additional services
- Tough to troubleshoot
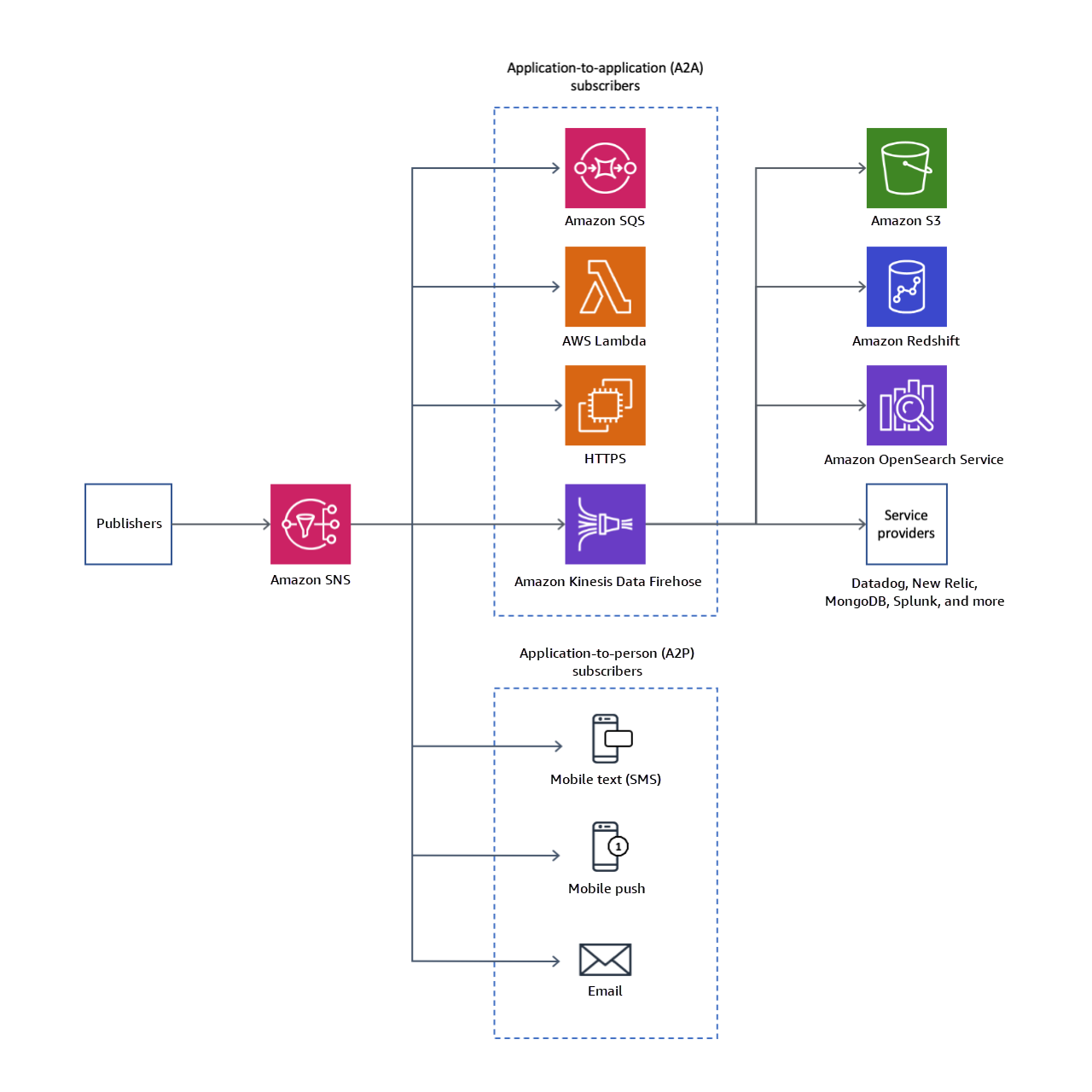
Amazon SQS
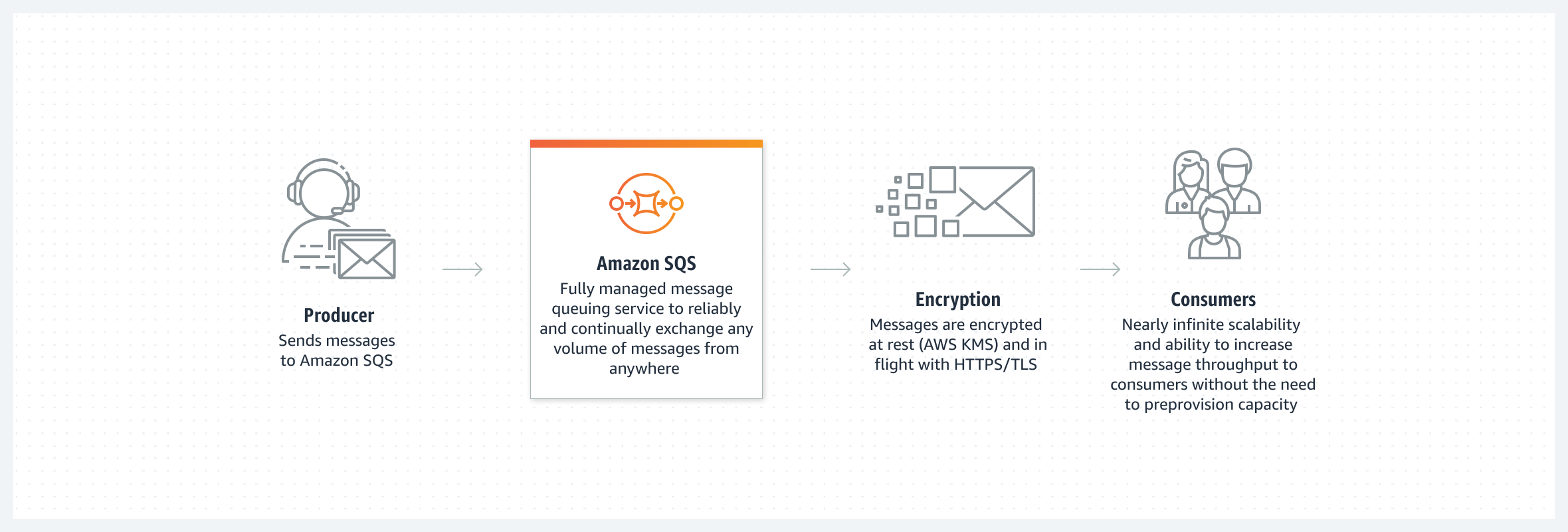
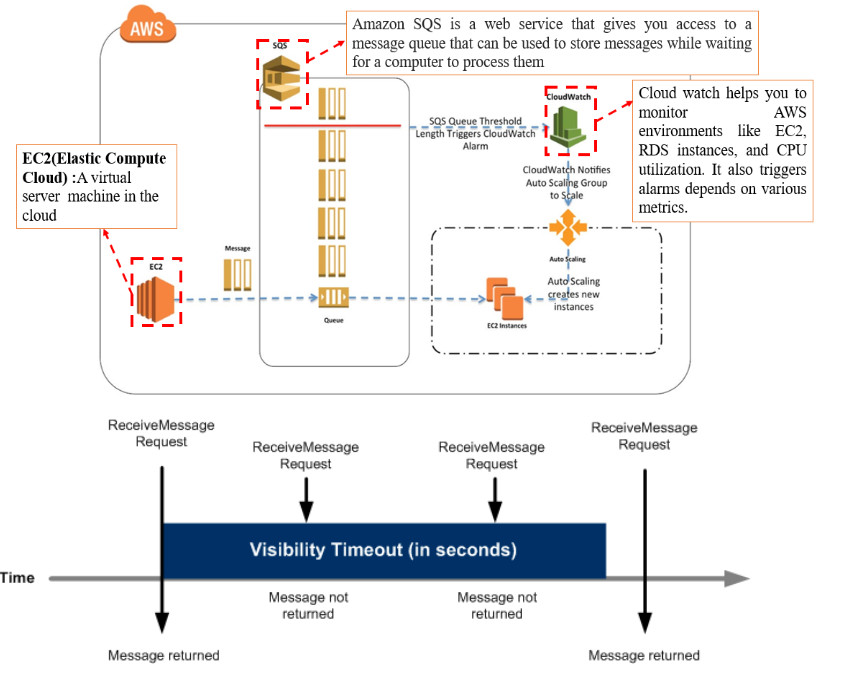 Messages can be max 256kb in size. Can be JSON, XML or plain text.
Message stored in queue temporarily
FIFO queues
Messages can be max 256kb in size. Can be JSON, XML or plain text.
Message stored in queue temporarily
FIFO queues
Advantages
- Decoupling Components: Enhances flexibility and independent scaling of microservices.
- Reliability: Ensures message delivery with redundancy and fault tolerance.
- Scalability: Handles virtually unlimited messages.
- Asynchronous Communication: Allows producers and consumers to operate independently.
- Managed Service: Reduces operational overhead with built-in scaling and fault tolerance.
- AWS Integration: Works seamlessly with services like Lambda, SNS, and CloudWatch.
- Cost-Effective: Pay-as-you-go model optimizes costs.
- Security: Supports encryption and IAM-based access control.
Challenges
- Message Ordering: Standard queues don’t guarantee order; FIFO queues may have lower throughput.
- Visibility Timeout: Requires careful management to avoid message duplication or delays.
- Message Size Limit: 256 KB limit may require alternate solutions like Amazon S3 for larger payloads.
- Message Retention: Messages are retained for up to 14 days, risking loss if unprocessed.
- Latency: Possible delays in processing during traffic spikes or polling.
- DLQ Management: Needs additional configuration and monitoring for failed messages.
- FIFO Queue Limits: Throughput is capped at 300–3,000 TPS.
- No Message Prioritization: Lacks built-in prioritization, requiring custom implementations.
Amazon SNS
Simple Notification Service allows to send notifications to large number of subscribers or endpoints.